Space exploration has always been a primary goal for humanity, pushing the boundaries of our understanding and opening up new frontiers. In recent years, data science has emerged as a pivotal tool, transforming the way we approach space technology. The ability to gather, analyze, and interpret extensive data has enhanced our understanding of the cosmos and changed the way we explore and navigate space. The success of Chandrayaan-3 is a significant milestone as it makes India the first country to reach the Moon's lunar south pole. This achievement has also garnered the interest of space agencies worldwide due to the potential presence of water ice. It's crucial to emphasize the role of data analytics in facilitating the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)'s moon landing mission.
Journey Through the History of Space Data
As we journey through space data history, it's clear that data science is crucial for exploring the cosmos, leading to achievements like Chandrayaan-3's moon landing.
-
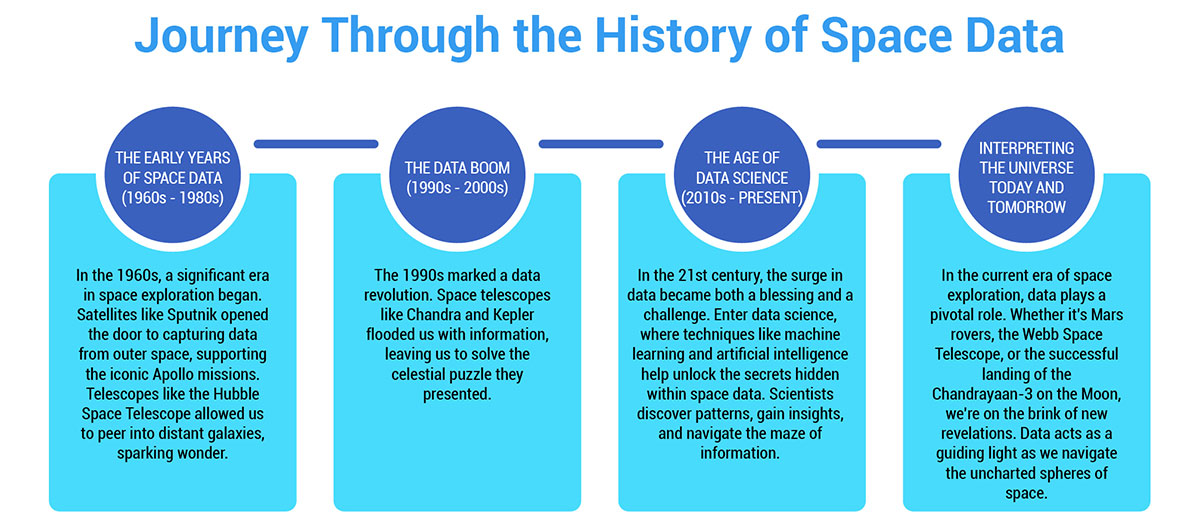
The Early Years of Space Data (1960s - 1980s):
In the 1960s, a significant era in space exploration began. Satellites like Sputnik opened the door to capturing data from outer space, supporting the iconic Apollo missions. Telescopes like the Hubble Space Telescope allowed us to peer into distant galaxies, sparking wonder. -
The Data Boom (1990s - 2000s):
The 1990s marked a data revolution. Space telescopes like Chandra and Kepler flooded us with information, leaving us to solve the celestial puzzle they presented. -
The Age of Data Science (2010s - Present):
In the 21st century, the surge in data became both a blessing and a challenge. Enter data science, where techniques like machine learning and artificial intelligence help unlock the secrets hidden within space data. Scientists discover patterns, gain insights, and navigate the maze of information. -
Interpreting the Universe Today and Tomorrow:
In the current era of space exploration, data plays a pivotal role. Whether it's Mars rovers, the Webb Space Telescope, or the successful landing of the Chandrayaan-3 on the Moon, we're on the brink of new revelations. Data acts as a guiding light as we navigate the uncharted spheres of space.
Chandrayan 3 Explained
In 2023, India launched Chandrayaan-3, its third lunar mission. Unlike its predecessor Chandrayaan-2, this mission includes a lander and rover but lacks an orbiter. The lander and rover are carried to the moon by a dedicated propulsion module, which also acts as a communication relay satellite. The lander maintains communication with both the rover and the Chandrayaan-2 orbiter for backup purposes. The mission's primary goal is to land near the moon's South Pole, a location previously unexplored by any nation, to conduct scientific experiments over a span of about 14 Earth days.
Key People Behind India’s Greatest Space Mission
Although it's the whole team whose efforts have led to the success of the mission, the three prominent figures who led to India’s Greatest Space Mission are:
- S Somanath: ISRO Chairman, took the helm in January of the previous year and quickly became a central figure in India's lunar mission. Before his current role, he directed key ISRO rocket technology development centers - the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC) and the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre. Currently, he oversees Chandrayaan-3, Aditya-L1 (a Sun study mission), and Gaganyaan (India's inaugural manned mission).
- P Veeramuthuvel: In 2019, P Veeramuthuvel assumed the role of Project Director for Chandrayaan-3, following his tenure as Deputy Director at ISRO's Space Infrastructure Programme Office. He played a pivotal role in Chandrayaan-2, the second phase of India's lunar exploration endeavor. Hailing from Villupuram, Tamil Nadu, he is an IIT-Madras alumnus.
- M Sankaran: In June 2021, M Sankaran took on the role of Director at the U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), where he oversees the design and construction of all of India's satellites for ISRO. Under his guidance, the URSC team is responsible for creating satellites that serve various critical purposes, from communication and navigation to remote sensing, weather forecasting, and planetary exploration.
The Significant Impact of Data Analytics on Space Exploration
Data analytics is important in contemporary space missions, encompassing data collection, processing, analysis, and interpretation. It plays a fundamental role in spacecraft design and trajectory optimization by employing mathematical models, simulations, and optimization techniques. Data analytics also transforms raw data from onboard instruments into meaningful information using signal and image processing, data mining, and pattern recognition. Additionally, it supports communication, navigation, and lunar exploration through techniques like error correction codes, encryption, and machine learning. This versatile process is a cornerstone of space missions, ensuring efficiency and success in the exploration of space and celestial bodies.
How is Chandrayaan-3 aided by data analytics?
Chandrayaan-3 employs data analytics in numerous vital facets of its mission, enhancing its operational efficiency and the likelihood of achieving success. Some of them are:
-
Propulsion Optimization
The propulsion system for Chandrayaan-3 is meticulously engineered, featuring bi-propellant thrusters that utilize monomethylhydrazine (MMH) as the fuel source and mixed oxides of nitrogen (MON-3) as the oxidizer. To achieve the highest operational efficiency and spacecraft stability, advanced data analytics plays a pivotal role in the design process. This involves the systematic analysis of data to determine the most advantageous configuration, strategic placement, and precise orientation of the thrusters and reaction wheels. These analytics-driven decisions aim to minimize fuel consumption, optimize thrust efficiency, and guarantee the overall steadiness of the spacecraft during its mission. -
Lunar Selection
Chandrayaan-3's critical landing site algorithm considers safety and scientific objectives by assessing parameters like slope, roughness, lighting, and thermal conditions. Data analytics, driven by high-res satellite imagery and machine learning, identifies lunar surface hazards. Additionally, optimization techniques enhance site selection by maximizing scientific value while minimizing risk. This versatile data-driven system ensures mission success. -
Spacecraft Communication & Navigation
Utilizing error correction, encryption, signal processing, data compression, and antenna design algorithms. These ensure reliable links with ground stations, orbiters, and satellites. Orbit determination and correction algorithms maintain precise trajectories. -
Payload Processing
Chandrayaan-3's scientific payload data processing involves various instruments:

- RAMBHA: Measures lunar plasma density and temperature.
- ILSA: Detects and characterizes moonquakes.
- APXS: Determines lunar surface elemental composition.
- ChaSTE: Gauges lunar regolith's thermal properties.
- LRA: Supports precise lunar orbit measurement.
- LIBS: Analyzes lunar surface elements using laser-induced breakdown.
Data analytics is essential for tasks such as filtering, noise reduction, and anomaly detection, ensuring data integrity and instrument reliability during processing.
The Obstacles Encountered During the Space Mission
ISRO Chairman S. Somanath emphasized that the mission's most challenging aspect lies in successfully launching it. The second pivotal moment entails the moon landing and its successful capture, as any miscalculation at this stage would render recovery impossible. The third crucial aspect involves the separation and on-time landing of the orbiter. To delve deeper into these challenges, Somanath stressed the need for meticulous planning and precision at each of these mission-critical stages, highlighting that any errors or deviations could have dire consequences for the entire mission's success.
- Large volume of data: Chandrayaan-3 will unleash a torrent of data with its high-res instruments and sensors, demanding immense memory, lightning-fast transmission, and supercharged processing.
- Data integrity: The safeguarding of data transmitted or received by Chandrayaan-3 could be jeopardized by malevolent incursions from cyber intruders or foes. This presents a conundrum in data transmission, as it requires robust methods to shield data against unauthorized entry or manipulation.
- Data multiplicity: The plethora of data amassed by Chandrayaan-3 can be attributed to a multitude of factors, including diverse instrumentation and sensors, varied operational modes and phases, distinct geographical locations and timeframes of observation, and a wide array of data types and formats. This gives rise to a data integration predicament, demanding adaptable techniques capable of managing heterogeneous, multi-modal, and multidimensional data.
Data-Driven Moon Landing
Data analytics played a vital role in Chandrayaan-3's successful Moon landing. The mission needed lots of data for precise navigation and landing. By looking at data from different sensors on the lander and orbiter, scientists and engineers could make smart choices during the mission. This helped them make the right turns, avoid problems, and use fuel efficiently. The lessons from data analysis were crucial in making sure the landing went smoothly and safely, making the mission a big success.
As space missions grow more complex, data scientists play a vital role in ensuring success. They contribute to various aspects, including predicting landing spots, lunar soil analysis, mission planning, software development, and data management. The increasing use of AI technology, as seen in Chandrayaan-3, highlights the growing opportunities for data analytics professionals in space.