Key Takeaways:
Key Takeaways:
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Types of Clouds
- Types of Cloud Computing
- Comparison among Top 3 Cloud Computing Providers
- Pros and Cons of using Cloud
- How to migrate to Cloud
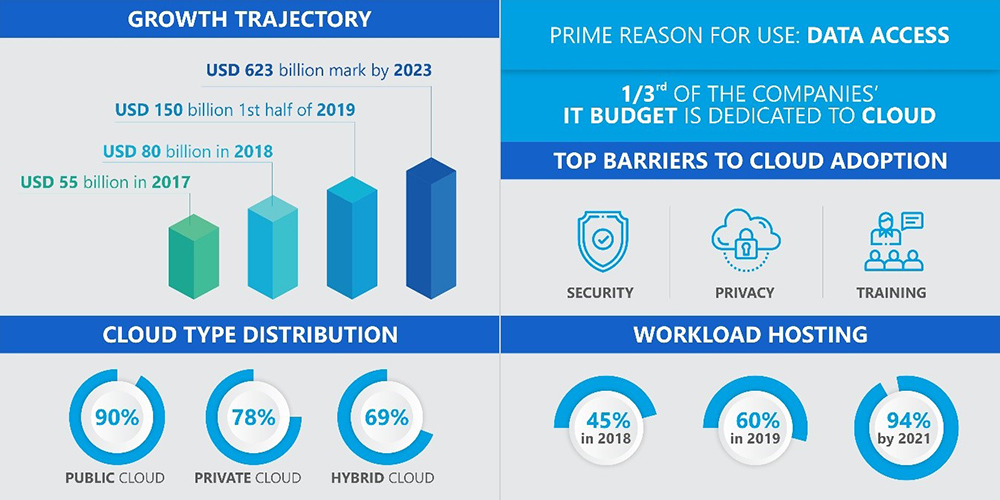
The US has the most thriving Cloud Computing market with approximate market size of USD 124.6 billion.
Why organizations are incorporating cloud computing:2019 saw a steep spike in the gig and freelance workers hiring. This trend is expected to escalate in the coming years. The International Working Group (IWG) says remote work is likely to become a norm within the coming five years. In these times of BYOD arrangement, organizations need much more bandwidth and flexibility wherein employees get the resources to work from anywhere, anytime. This is where Cloud Computing comes into the picture.
Recently, we witnessed 4.1 billion people accessing the internet and generating more than 2.5 quintillion of bytes of data daily. Cloud Computing means dispersal of computing services over the internet. This includes storage, servers, software, networking, analytics, databases, and intelligence. Cloud users pay for the services they use. It lowers operating costs, improves the efficiency of the infrastructure and helps in scaling businesses up. Organizations use Cloud for “data backup, disaster recovery, email, virtual desktops, software development, and testing, big data analytics, and customer-facing web applications.”
Cloud computing is helping:
- Healthcare companies facilitate personalized treatment plans
- Financial companies drive real-time fraud prevention and detection
- Video game makers deliver online games
Three models are available:
- Public Clouds deliver services on the internet
- Private Clouds are used to access information within the organization
- Hybrid Clouds are a mix of the two above
Large enterprises use private clouds more while small and medium organizations usually opt for public clouds.
Types of cloud computing:Infrastructure as a Service: (IaaS): These are the fundamental building blocks for Cloud IT. IaaS facilitates access to networking features, computers and storage space.
Platform as a Service: (PaaS) PaaS takes care of the infrastructure management and the clients only need to deploy and manage their applications.
Software as a Service: (SaaS): SaaS gives the complete product, operated and managed by the service provider. Users can freely use the software.
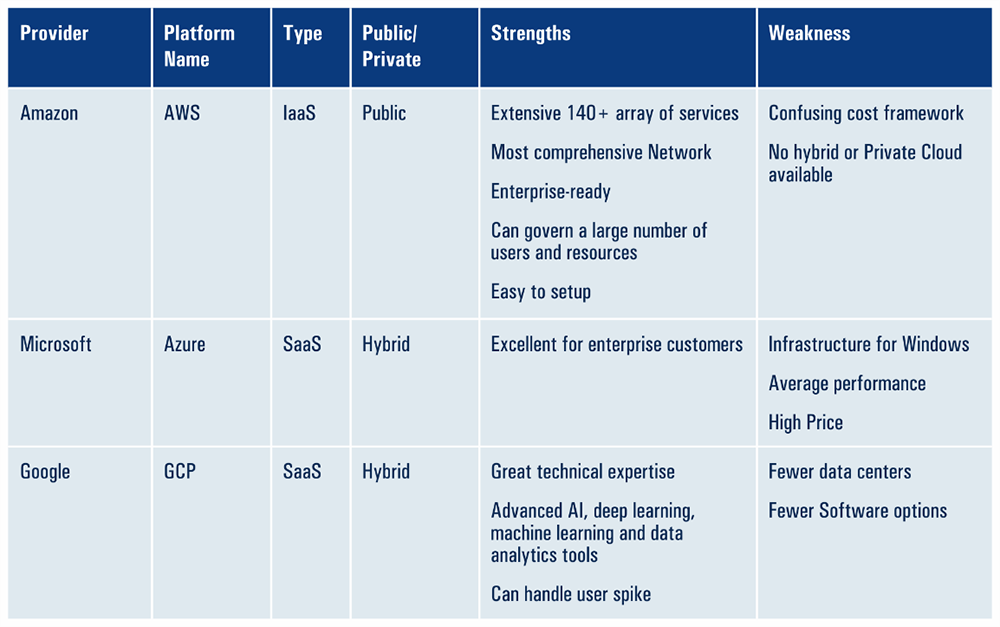
Top three cloud computing providers:Though Amazon, Microsoft, and Google have the major chunk of the market share, other players like SalesForce, Adobe, SAP, and Oracle are rooting themselves in SaaS and, Alibaba and IBM have delineated their pie in IaaS. Amazon has dominated the IaaS market for more than a decade now. Other smaller players are mushrooming, albeit at a relatively slower pace. Cobalt Iron’s enterprise-grade backup and recovery solution is renowned for its cheaper cost, reliability and automation.
Here’s a snapshot of the strengths and weaknesses of the top three providers:
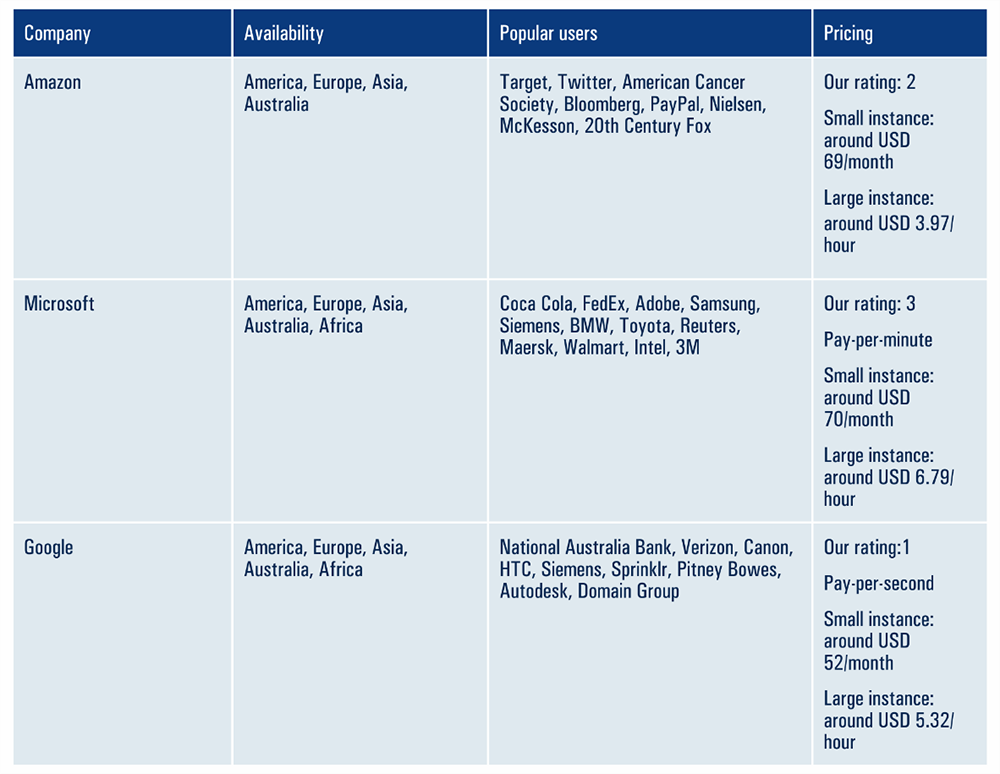
Availability and Users:
Pros:
- Cloud is cheaper as buyers only pay for the services they use
- It lowers operating costs, improves efficiency and helps quick scaling up of businesses
- Overall savings come close to 15% for large organizations and 36% for small and medium organizations
- Cloud is a boom for businesses that are season-based
Cons:
- Two-third of organizations say security is a major impediment in cloud computing
- 60% of users worry about privacy, governance, regulatory and compliance issues
- 50% of the organizations lack sufficient skills
- 75% of IT professionals find privacy and data security more complex on the Cloud
If you are looking for smooth access to a wide range of technologies, faster innovation, and creation capabilities then try using Cloud services. Choosing the right service provider can be the most important decision. Chose the service provider according to the available features, your budget and your requirements. Organizations usually opt for a multi-cloud strategy. So here’s your chance to device that perfect mix.
93% of beginners in cloud computing begin with AWS and Azure.
If you are a small-sized organization or a Startup, then pricing can be the main concern for you. The pricing of clouds is dynamic and will depend on:
- Specifications
- Number of Servers you want
- The volume of Data you want to store and transfer
- Your operating system and software
- Short term or long term service
- Pay duration: hour, minute or month or pay-as-you-go for long term service
- Location of cloud data center
Happy Cloud Computing!