There’s more to data science than mere data science. Not to say that the science is any less important, but like all things data, the construct forms the basis of the accuracy. It is virtually impossible to be dealing with big data and not have the engineering to create and streamline it to form the basis of analysis or even machine learning, for that matter. This is precisely where a Big Data Engineer’s role comes into play. Big Data Engineers, highly sought after by employers today, are responsible for the structure and form of the final data that is analyzed and acted upon. In the hierarchy of data science and machine learning, the foundations are laid almost entirely by big data engineers.
Functions of a Big Data EngineerBig data engineering is not just one function, it’s a series of intertwined functions that meld into each other, based on the organization’s data processing needs and the complexity of disparate datasets that require processing.
If you asked most big data engineers, they’d mention ETL (extract, transform & load) as the most common industry jargon for what they do. There is more to the role of a big data engineer, however.
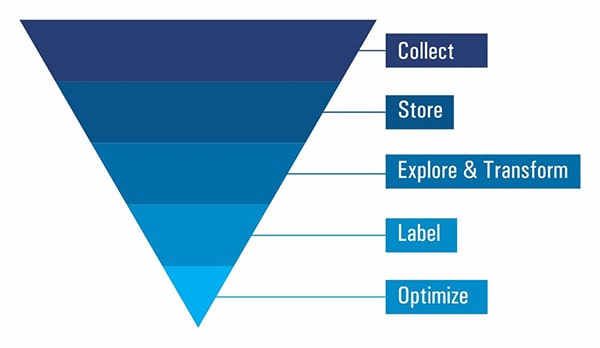
Collection - Collection of data, whether in sets or real time, is the first step of the big data engineering process. This includes identifying the correct sources of data ingestion, and arranging for the data to flow into the central repository for further storage, whether in fixed sets or real-time.
Storage- Once collected, data is stored in a central repository, which could range from a NoSQL database to a data warehouse or even a data lake. The big data engineer is responsible for the safe storage of data according to the enterprise needs.
Explore and Transform - This is where all the sweat comes into play. Data, no matter how big, is useless unless it is transformed into a suitable form for analysis and modeling. This stage includes exploratory data analysis, removal of anomalies and overall preparation of the data for further processing, visualization, and modeling.
Label- On most occasions, incoming data needs to have the right classifiers attached to them. Also called labeling, this function helps in the segregation of data according to its nature and form, for the next stages in the entire big data life cycle.
Optimize- Optimization usually follows the labeling function, and is exactly what the name suggests - further performance tuning of all previous stages in the big data engineering life cycle to achieve greater efficiencies and accuracy.
In the very broadest of terms, the role of a big data engineer is to collect and transform the available enterprise data in a way that it can be analyzed and modeled as per the requirements of the organization.
The Demand for Big Data EngineersAccording to several industry experts, there is a requirement of two to five big data engineers for every data scientist in an organization. They are also paid significantly higher than their average computer science and developer counterparts. According to employment portal Glassdoor, the base pay of big data engineers stood at $116,000 per annum. Not only are the salary scales massive, the demand has shown significant past growth, consistently, and is only set to grow at a more rapid pace with the advent of Industry4.0 and artificial intelligence.
The SBDE Credential - Your Pass to the Career SuperhighwayApart from a great understanding of data management lifecycle, there are also several technical proficiencies that Big Data Engineers need as must-haves in their skill portfolio. These include understanding of NoSQL databases, deep understanding of the Apache Hadoop platform, sufficient scripting prowess using Pig and Hive, understanding of R and Python, and a whole host of others, all of which are covered under the Dasca SBDE curriculum. In fact, Dasca certified Senior Big Data Engineers are widely respected and sought after by employers worldwide. So get your professional bragging rights in the world of Big Data Engineering now!